Arkansas GDP up 2.5% in the first quarter, personal income up 6.1%
by June 28, 2024 10:19 am 466 views
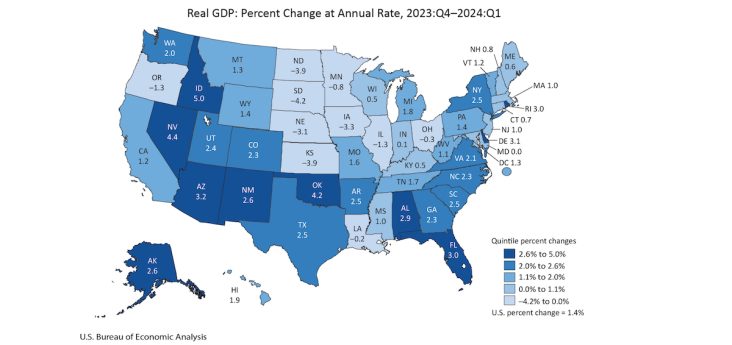
Arkansas’ real gross domestic product (GDP) rose 2.5% in the first quarter of 2024 compared to the previous quarter, above the national rate of 1.4%, and ranking 11th in the nation. The state’s personal income rose 6.1%, below 7% nationwide, and ranking 38th among all states.
Real GDP increased in 39 states and the District of Columbia in the first quarter of 2024, with the percent change ranging from 5% at an annual rate in Idaho to a 4.2% decline in South Dakota, according to a Friday (June 28) report from the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA).
Personal income, in current dollars, increased in all 50 states, with the percent change ranging from 9.5% in South Carolina to 0.6% in North Dakota.
Arkansas’ GDP growth was higher than all contiguous states except for Oklahoma at 4.2%, with Texas also at 2.5%. Arkansas’ personal income growth of 6.1% was lower than all contiguous states except for Mississippi which rose 5.1%.
Sectors contributing to Arkansas’ GDP growth included agriculture/forestry (up 2.01%), retail (up 0.59%), construction (up 0.24%), finance (up 0.24%), health care (up 0.23%), and transportation/warehousing (up 0.23%). Arkansas sectors showing GDP decline included durable goods manufacturing (down 0.68%), non-durable goods manufacturing (down 0.21%), wholesale trade (down 0.2%), and utilities (down 0.09%).
Personal income growth in Arkansas was boosted by an 8.2% growth in transfer receipts, and a 5.5% growth in net earnings. Income from dividends, interest and rent grew 5.3%. (Personal current transfer receipts are benefits received by persons from federal, state, and local governments and from businesses for which no current services are performed.They include retirement and disability insurance benefits (mainly social security), medical benefits (mainly Medicare and Medicaid), income maintenance benefits, unemployment insurance compensation, veterans’ benefits, and federal education and training assistance.)
NATIONAL NUMBERS
In the first quarter of 2024, real GDP for the nation grew at an annual rate of 1.4%. Real GDP increased in 15 of the 23 industry groups. Retail trade, construction, finance and insurance, and health care and social assistance were the leading contributors to growth in real GDP nationally. Construction, which increased in 46 states and the District of Columbia, was the leading contributor to growth in 10 states including Idaho and Nevada, the states with the first- and second-largest increases in real GDP.
Agriculture, forestry, fishing, and hunting, which increased in 34 states, was the leading contributor to growth in 6 states including Oklahoma, the state with the third-largest increase in real GDP. In contrast, this industry was the leading offset to growth in 9 states including South Dakota, North Dakota, Kansas, Iowa, Nebraska, and Illinois, the states with the largest decreases in real GDP.
In the first quarter of 2024, current-dollar personal income increased $396.6 billion, or 7% at an annual rate. Nationally, earnings, transfer receipts, and property income (dividends, interest, and rent), all contributed to the increase in personal income.
Transfer receipts increased in all 50 states, while growing 16.8% nationally. The percent change in transfer receipts ranged from 24.8% in Utah to 6.7% in Mississippi.
Transfer receipts was the largest contributor to growth in personal income in 20 states, including South Carolina, the state that led the nation in personal income growth. The increase in transfer receipts in the first quarter of 2024 reflected a 3.2 percent cost-of-living adjustment for social security recipients, along with increases in refundable tax credits and Medicaid benefits.
Earnings increased in 47 states, while growing 4.7% nationally. The percent change in earnings ranged from 7.2% in Alabama and Delaware to a 4.5% decline in North Dakota. Earnings increased in 21 of the 24 industries. Earnings was the largest contributor to growth in personal income in 26 states.
Property income increased in all 50 states, while growing 6% nationally. The percent change ranged from 9.2% in Texas to 3.6% in Illinois.
